In the beginning, humans used solids, especially wood and grass, as their main fuel sources. Over the centuries, industrialization has led to a variety of liquid fuels derived from oil, including kerosene, gasoline, and other derivatives. But with dwindling petroleum reserves, biofuel engineers are beginning to use solid fuels derived from wood, plants, grasses, algae, and aquatic plants to create large amounts of renewable energy. All of these resources are part of new and plentiful advances in biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. (see Plant Biotechnology for Sustainable Production)
Human manufacturing, farming, and cities create wood and crop residues and a significant amount of clean urban waste. Brazil, for example, is the largest producer of eucalyptus pulp and sugarcane in the world and makes use of this otherwise useless resource in biomass power plants. Biomass includes dozens of exotic plants like Miscanthus grass, but it also can include garbage.
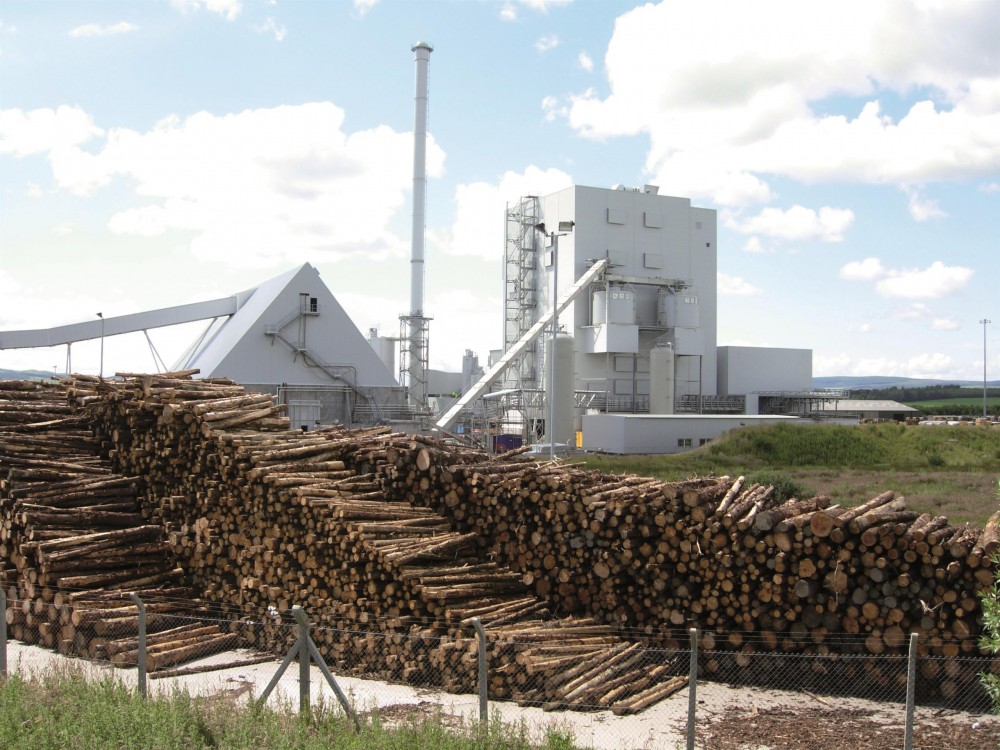
More Biomass Power Plants
The world is now seeing an uptick in the number of biomass power plants currently installed or coming online. But biomass power plants currently emit high levels of particulates, including soot, ash, and carbon monoxide. In order for biomass power plants to be viable, they must become cleaner. But, according to a report by Goldman Sachs, “5 Types of Clean Energy,” biomass makes the grade.
Fortunately, scientists and engineers are learning from the track records of existing biomass power plants. A book, “Lessons Learned from Existing Biomass Power Plants” published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), summarizes lessons learned from 20 biomass power plants.
New Technology Improving Biomass Power Plant Performance
Today, biomass power plants are using pellets created from renewable sources to produce power. The pelletizing process improves the combustion and gasification of biomass resources. In addition, improved design, planning, and construction of biomass power plants are leading to improved efficiency.
Each type of renewable resource has its own emissions, operational behavior, residues, costs, and efficiency. One current focus is to assess the technical possibilities of reducing CO2 emissions from specific types of biomass resources.
The main focus of new strategies is to produce energy from biomass materials more efficiently, to improving heat generation technologies, improving renewable biomass processing, and including carbon capture and storage capabilities to improve performance.
Following is a YouTube Playlist of 6 videos about Biomass Power Plants: