Decentralized finance refers to the financial systems that operate with no public, private or official supervision. These systems do not rely on the sharing or investing of monetary capital by private institutions, but are instead formed through decentralized networks, rooted in a common online ledger.
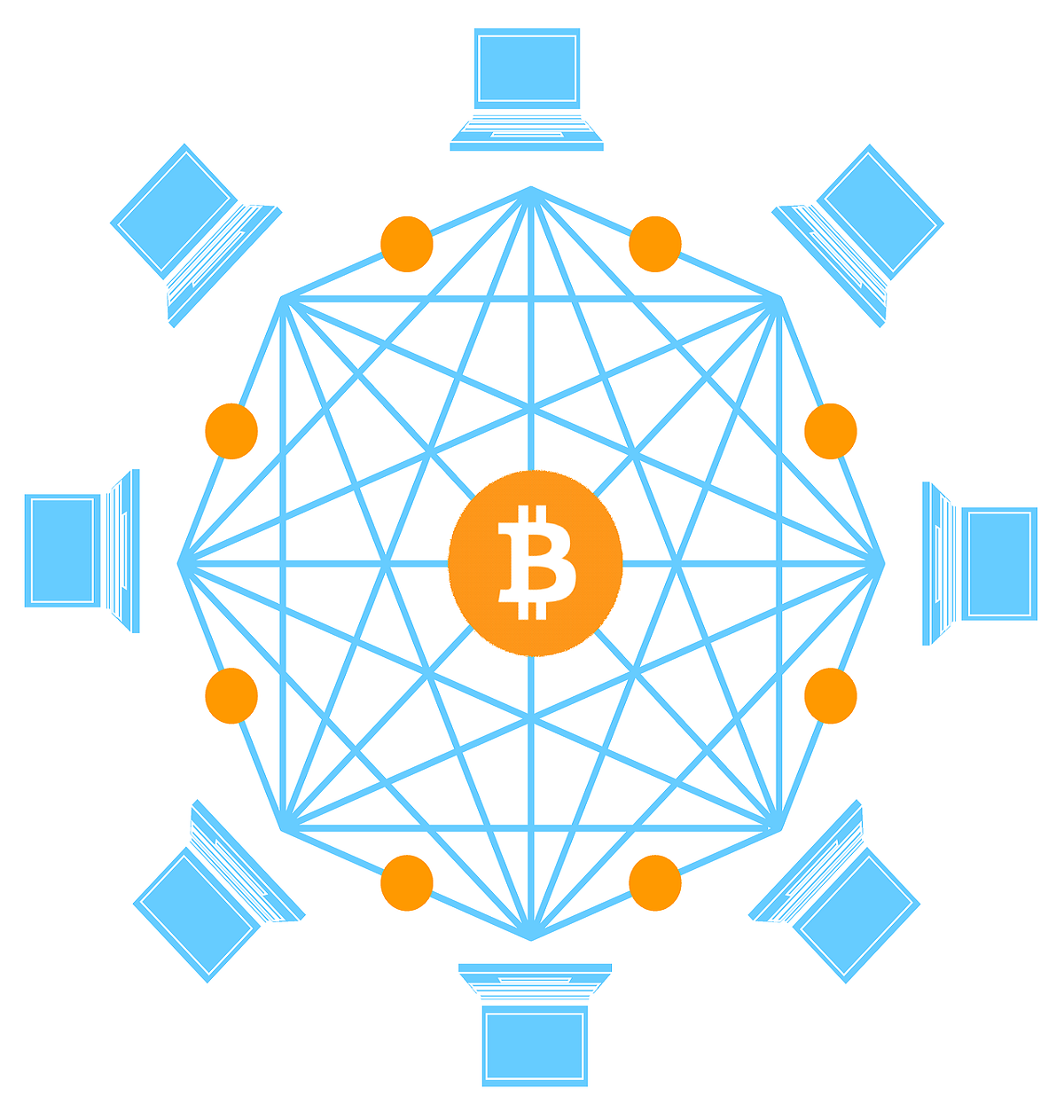
Blockchains make this process possible. Decentralized systems utilize computer technology to generate a digital blockchain or “tangle” network of databases. This technology allows each participant in the network to provide various services to the network in exchange for payment in its native currency.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized financial systems provide a more flexible way of organizing and processing financial asset transactions. These systems allow users to organize funds in various ways, such as distributing shares among many participants, or to charge fees on a per-transaction basis. They also allow multiple parties to apply for financial instruments, without the need for a central authority to approve such transactions.
Decentralized financial systems also use blockchain technology to integrate decentralized apps (dApps) into networks, the shared virtual tool that users use to engage in financial transactions. Because these apps are integrated into the underlying network, a user’s transactions are unaffected by outside forces, such as an external hack or the actions of counterparties.
If a system is centralized, anyone who controls the network has a significant amount of control over what users can and cannot do. If an individual wants to purchase a product or access a service from another party, the network may prevent them from doing so.
Decentralized networks are very different from the traditional internet: They operate at a different scale, based on how much value is in each block and the amount of tokens the network can support.
Blockchain Security
Blockchain-based networks rely on cryptography to ensure the security of each block. Each block has a unique private key, which the network uses to ensure that transactions and the network itself cannot be changed. This allows the network to continue to function despite outside threats. Bitcoin is one of the most popular examples of a blockchain-based currency because it operates by using cryptography to make each block unique.
The network consists of several nodes that each validate blocks and create transactions and consensus. Because of the size of the network and the amount of data involved, it is slow to process. To compensate for this, fees are often paid to nodes. In traditional financial markets, central clearing houses validate transactions and then move the money. In decentralized systems, the money enters the network through a point-of-sale system, where the user sends their data to the recipient, who places the money into a corresponding wallet.