IndustryTap has written about NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO-2) and the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS), among others. These missions are focused on understanding the earth and its place in the solar system.
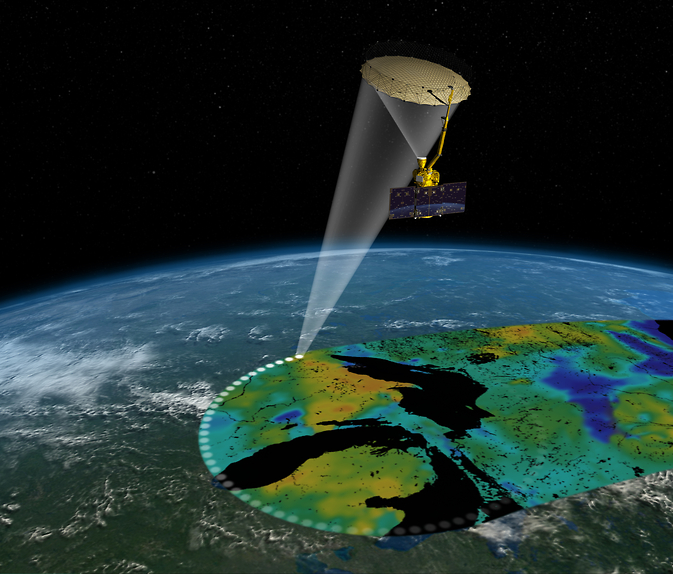
Later this week NASA will launch the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite. The purpose of SMAP is to understand “soil profiles“, specifically their moisture content, around the globe. The mission will provide unprecedented accuracy and resolution in creating a global map of soil moisture; this map will be updated every three days so that trends can be studied.
According to NASA Goddard Space Flight Center scientist Randy Koster, SMAP will allow the identification of specific regions where soil moisture is heavily influenced by local weather patterns. In addition, “SMAP will improve soil moisture measurements in the United States, but it’ll improve measurements in the Sahara Desert substantially.”
The Earth’s “Hotspots”
According to Koster, some of the world’s hotspots include Northern India, the African Sahel region south of the Sahara Desert, and the U.S. Midwest and West. Humans depend on a tiny fraction of the world’s water and understanding moisture on the earth’s surface and locked in soils is important to the long-term promotion of plant growth and providing food.
Moisture evaporation rates will also be studied. As part of this, the relationship between temperature, soil moisture, aeration, the accumulation of organic matter in soils, and the way in which shading from trees and other plants affects soil moisture and evaporation will be examined.
Related aricles on IndustryTap:
- Satellite Technology Detecting “Sea Mountains”, Mapping Ocean Floors
- Will NASA’s New $280 Million Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO-2) Help Resolve The Climate Change Debate?
- NASA Releases Computer Codes for Over 1,000 Programs to the Public
References and related content: